X-Vagus
The Vagus nerve is a mixed nerve containing afferent, motor and parasympathetic fibres.
Innervation
Sensory
- Pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, external ear
- Aortic bodies, aortic arch
- Viscera of thorax and abdomen
Motor
- Soft palate, pharynx, larynx, upper oesophagus
Parasympathetic
- Viscera of thorax and abdomen
Function
Afferent
- General sensation of pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, tympanic membrane, the external auditory meatus and part of the concha
- Chemoreception in aortic bodies and baroreception in the aortic arch
Motor
- Speech and swallowing
Parasympathetic
- Parasympathetic innervation of the heart, lungs and digestive tract
Anatomy
Many of the central connections of the vagus nerve are shared with the glosspharyngeal nerve.
Somatic afferents terminate in the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex. Fibres carrying taste information terminate in the tractus solitaries. Parasympathetic fibres originate from the dorsal nucleus and nucleus ambiguous. Somatomotor fibres also originate from the nucleus ambiguous.
The vagus nerve leaves the skull via the jugular foramen.
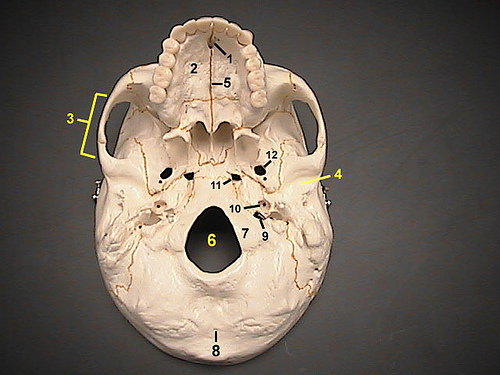
Label 9 is the jugular foramen
Image courtesy of https://www.flickr.com/photos/guccibear2005/166907714/ under the creative commons license.